Selecting a phosphate ester will depend on what your needs are with respect to the surface tension, solubility, foaming, and wetting needs of your system. To select the right product for your application, contact your Silver Fern Chemical sales representative.
Phosphate Esters
Phosphate esters are anionic surfactants produced by using phosphoric acid to esterify various alcohol or fatty acid molecules. The phosphate group allows the fatty alcohol or fatty acid to change its physical and chemical properties resulting in alternative use capabilities.
Depending on the number of alcohol groups reacted with phosphoric acid, we can have:
- Monophosphate esters: One alcohol group reacts with phosphoric acid.
- Diphosphate esters: Two alcohol groups react with phosphoric acid.
- Triphosphate esters: Three alcohol groups react with phosphoric acid.
Product Details |
|
|---|---|
Formula: |
R-O-P(=O)(OH)₂ |
CAS Number: |
126-73-8; 126-71-6; 78-51-3; 115-86-6; 1330-78-5; 13674-84-5; 13674-87-8; 115-96-8 |
Also Known As: |
Organophosphate; Tributyl phosphate; Triisobutyl phosphate; Tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate; Triphenyl phosphate: Tricresyl phosphate; Tri-(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate; Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate; Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate |
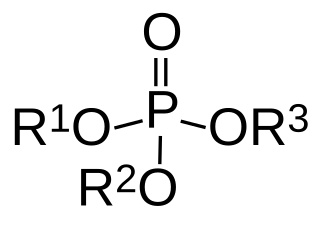
Structure: |
|
applications:
Phosphate esters are highly versatile surfactants that can be used for a wide range of applications. The primary advantage of phosphate esters over other surfactants is their alkali stability and solubility. They are excellent hydrotropes (water-loving molecules) and are effective coupling agents that display excellent wetting, emulsification, and detergency.
Phosphate esters are used widely in emulsion polymerization, metal finishing, household, industrial and institutional cleaners, textile preparations, lubricants, and metal working fluids.
Being stable in high alkali concentrations makes these products highly effective in heavy duty industrial or household cleaners and degreasers, where high active heavy duty products are required.
Phosphate esters also exhibit good corrosion inhibition properties. This makes them useful in lubricants and anti-wear additives. They are also used in the manufacture of greases, drawing compounds, chain belt lubricants, gear oils, and hydraulic fluids.
Typical Specifications
Data is representative of average lots;
data taken from specific lots may vary.
Appearance |
Colorless, pale yellow, amber, or brown viscous liquid |
Boiling Point, °C |
289 (decomposes) |
Density, g/cm3 |
0.9727-1.020 |
Flash Point, °C |
146 |
Melting point, °C |
−80 to −70 |
Molecular weight, g/mol |
266.31 |
Odor |
Odorless |
Purity, % |
99 |
Get a Quote?
We want to hear from you and will respond promptly


Distribution Locations Across USA